Knee Arthroscopic Procedures
The conditions that most often require arthroscopic surgery for Knee are:
- • Meniscaltears
- • Cartilagedefects(wearing orinjury ofcartilagecushion)
- • Anterior/posteriorcruciateligament tears withinstability
- • MedialPatella femoralligamenttear
Knee Surgery
The knee is a hinged joint made up of three bones held firmly together by ligaments that stabilize the joint. The bones that meet the knee are the upper leg bone (the femur), the lower leg bone (the tibia) and the knee cap (the patella). The bones inside the joint are line by a smooth protective layer called the articular cartilage, which allows the bones to glide smoothly upon each other.
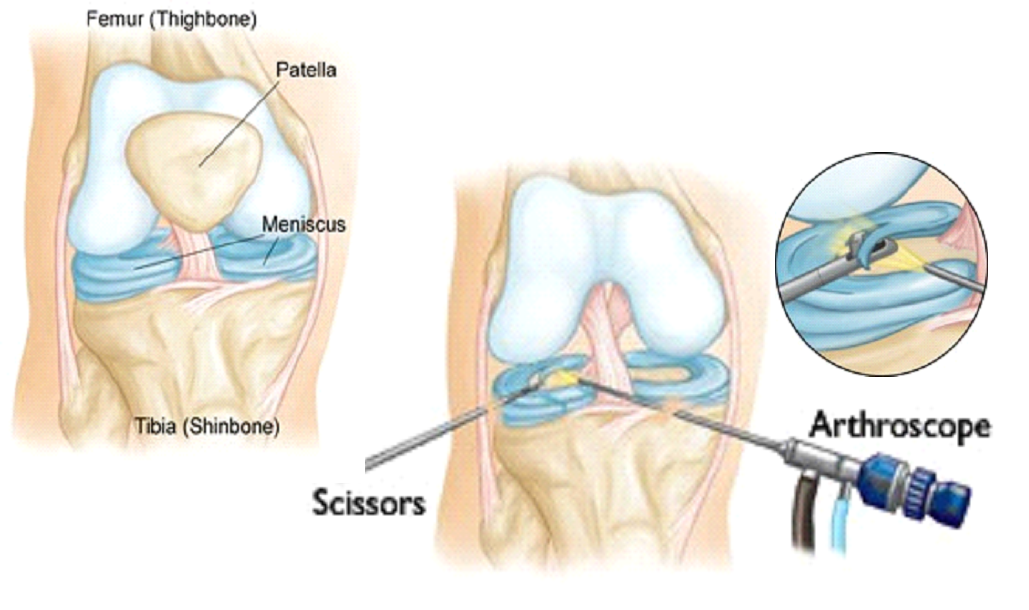
Meniscal Injury
The Menisci are two pads of the fibrocartilage on either side of the knee that act as cushions or shock absorbers. They also help distribute the weight load inside the knee . Most tears of the meniscus result from a sudden twisting movement of the knee , as in sports injuries . As the knee bends and twists, the meniscus may be pinched between the bones. This is often accompanied by a " popping sensation; and the knee is likely to swell a few hours after injury. Sometimes, the menisci may become damaged or torn, due to aging.
Treatment
All types of meniscal tear can be treated by arthroscopy. The treatment involves either trimming away the torn piece of the meniscus with miniature motorized instruments or repair of the meniscus when indicated.
1
2
3
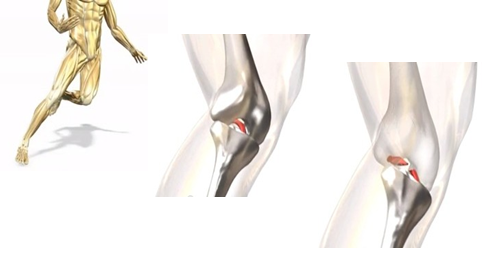
Ligament Injury
Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that fasten the bone ends together and stabilize the joint. Ligaments may be torn by sudden twisting motions of the knee beyond its normal range, during sports like Basketball, Volleyball, Cricket, Kabaddi or during road accidents.
The two main ligaments that can be reconstructed with arthroscopic surgery are the "anterior cruciate ligament" (ACL) and the "posterior cruciate ligament" (PC L). These cruciate ligaments restrict the forward and backward motion of the knee and its rotation. Treatment for ligament injury most often involves reconstruction through arthroscopy, utilizing the hamstring tendons or patella tendon as graft from the patient's own body.
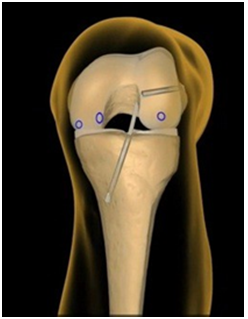
Results of this technique are extremely good. Other ligaments around knee which needs treatment are, PLC, MCL, LCL.
Cartilage Defect and OCD
This is a condition in which the cartilage surface lining the knee softens, sometimes to the point where the articular surface cracks, giving it an irregular surface (Chondromalacia). This may cause discomfort in the knee especially while using the stairs. If the problem does not respond to medication or physical therapy, the surgeon may choose to smooth the rough areas of the cartilage using arthroscopic surgery.
OCD is another condition wherein a small segment of cartilage along with the underlying bone gets disintegrated suddenly due to genetic problem. It occurs in relatively younger patients. Maintaining normal articular cartilage is very crucial for normal functioning of the knee.
Treatment
Conventionally it was treated by making holes in the deficient area where new cartilage grows but the quality of this cartilage is always inferior to the original cartilage. Most recent treatment technique is called AC! wherein a new cartilage is grown in laboratory by means of cloning technology of patients own cartilage cells and implanted into the deficient site. State of the art technique is all arthroscopic treatment of such disorders.
Loose bodies within the knee
Accidents can cause a fragment of cartilage or bone to come loose and float around the joint. Sometimes arthritic conditions may also cause loose bodies inside the joint. Depending on the size and location of the fragment , the orthopedic surgeon may decide to reattach it or remove it entirely using the arthroscope.
Osteoarthritis
Due to old age , most joints in the body, including the knee , may suffer from wear and tear. This results in pain and discomfort. If medication is not able to control the discomfort, the surgeon may choose to treat arthroscopically by shaving and smoothening the roughened surface of the bone and trimming of any damaged meniscus. Cleaning out the debris often helps reduce the pain.
